Introduction
With the acknowledgment of the standards of an efficient chain of supply, proceeding towards the food industry’s supply chains, comes into existence of another important consideration property in the SCM (supply chain management) is it’s, “Grade of Safeness”, where the environmental focus especially the temperature parameters in the production, transportation and storage of the raw materials and the finished produces, in the chain resides. This essential factor is endorsed with the modern (HARPC) Hazard Analysis and Risk-Based Preventive controls known as the FSMA (Food Safety Modernization Act), a revolutionary approach, put in place measures to avoid the foodborne maladies and ascertained to be effective in impeding contamination.
Business Case
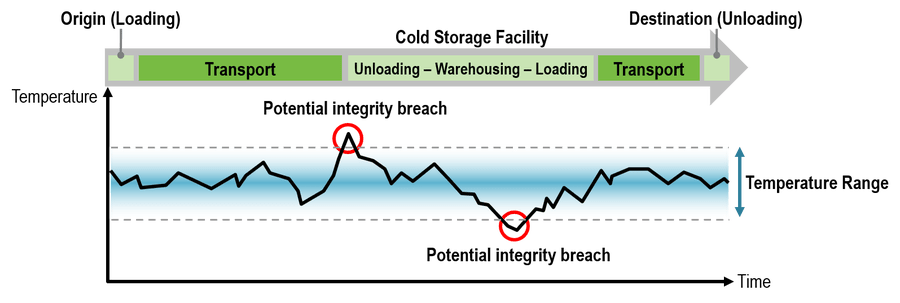
As a counterpart to the discussion of the FSMA, one of the leaders of the Sri Lanka’s food businesses organization that adheres to the rules and regulations of FSMA was encountered by SenzMate Technologies. The organization renowned for their enticing array of produces especially Jams and Fruit Juicing production, where temperature contributes as a substantial factor in the determination of the nutritional quality of the final production(sauces, chutneys, pickles, Jams, cordials, fruit drinks, concentrate Juices, etc.). Whilst, an increase in temperature beyond certain boundaries can drastically reduce the food value and sensorial properties of the final commodity.
The firm addressed it’s essentiality to enhance and endeavor the strict abidance of FSMA regulation in their production. Hence, bore the organizational decision to achieve a proactive step towards temperature supervision of its cold rooms and refrigerator trucks that ,stores and transports the perishables, that are engaged in the supply chain operations. Thus, the threshold of a digitized monitoring, analytics and hazard warning system together with a plethora of added beneficiary solutions was introduced to the organization that bestowed to a safer yet effective supply chain management.
Solution
The SenzMate Technologies’ Polar System, established with the determination of satisfying the FSMA compliances comprised with a collection of food health plans of Hazard Analysis, Preventive Controls, Monitoring Procedures, Corrective Actions, Verification and Record Keeping, reached it phase of deployment with myriads of expectation in the betterment of its supply chain and strict cooperation towards the regulations.

Action Taken
The deployment proceedings of the Polar System in the organization involved the adaptation of several sensors, polar devices, customized cloud architecture, warning system and mobile applications: That alleviates the processes of automated real-time precise data accumulation of the perishables , maintenance of accurate temperature levels in respect to the subjected locations and spaces of the transportation trucks paired with tracking facilities, timely alerts to the maintenance team of the organization, historic data availability and accessibility for quality auditing and report generations, in combination with user-oriented and comprehensive user interfaces built in terms of facilitated utilization and upgradation.
Results
In accordance to the practices of years, without an exception, SenzMate Polar System as always, have emerged it’s excellence and efficacy, by transforming the organization’s system’s expectations into a reality with complete client satisfaction. In the peak of it’s potentiality the system achieved its series of expected functionalities from, assuring optimized commodities quality with the maintenance of absolute focus on temperature in the recurring storage and transportation processes in the organization, instantaneous alerts to avert hazardous events as a result temperature fluctuations, to acquirable precise significant data ultimately, as a requirements of the FDA regulations and for future business based judgements, with improved system capacity of additional advantages to the organization by means of reduction in cost of electricity, minimization in food deteriorating and wastages and many other cost declines through avoidance of unfriendly criteria.